Introduction
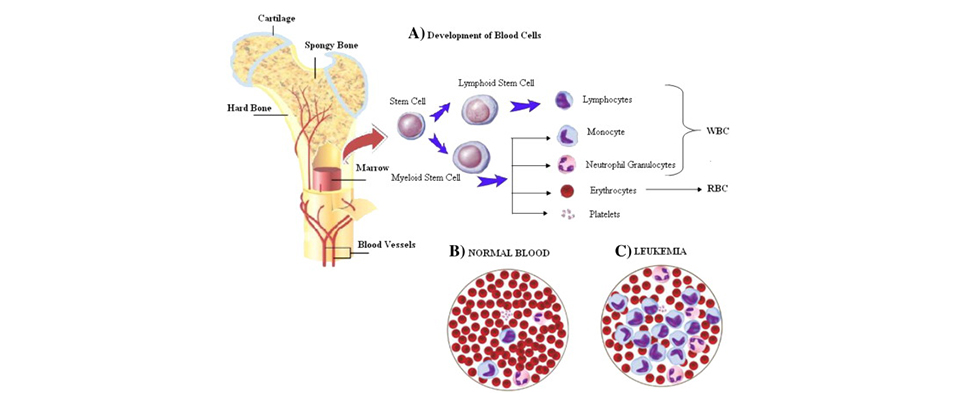
Leukemia is otherwise called blood cancer because it is the cancer of the blood cells. Platelets, red blood cells (RBCs) and white blood cells (WBCs) are the different categories of blood cells. Leukemia is considered as the cancer of the WBCs. WBCs are an integral part of the immune system since they protect the body from viruses, fungi, abnormal cell and bacteria. Leukemia occurs when the WBCs fails to function normally. They also can divide faster and crowd out healthy cells.
The main symptoms of Leukemia include:
- Sweating
- Weakness
- Weight loss
- Bone pain
- Red spot on the skin
- Fever
- Bleeding
Type of Leukemia:
Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia (ALL): It accounts for about 80% of the blood cancer and is common among children. It starts slowly but escalates suddenly. The affected cells can spread into the central nervous system and affect the spinal cord, and the brain eventually.
Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML): AML is always called acute myelogenous and is common in adults than in children. Environmental factors can aggravate the symptoms. Apart from Chemotherapy, which is the main treatment, a bone marrow transplant may also be suggested.
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL): The most common type of leukemia in adults it starts in the cells that become the WBCs. The chronic leukemic cells do not mature completely, and they look normal. Unlike the other cells they do not fight infections and tend to survive longer than the normal white blood cells. This cancer takes a very long time to manifest in any kind of symptoms.

